It’s difficult to pinpoint the start of the rally, but it accelerated in earnest in early March for no apparent reason other than investors arbitrarily decided to collectively increase risk-taking. This seems like a classic case of ‘making one’s own reality,’ given that the economic picture continues to deteriorate, and “positive” developments were limited to an increase in government intervention and stimulus plans. But, perception is everything in financial markets, and if investors collectively decide they want a rally, then a rally will indeed obtain.
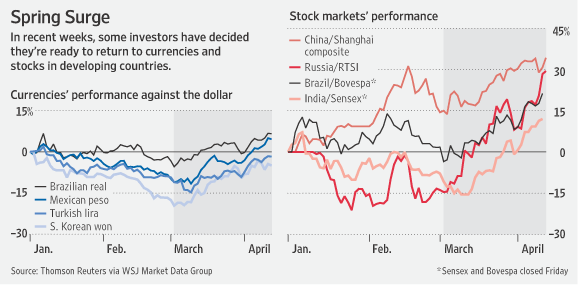
In the case of emerging markets, the rally has certainly surpassed all expectations. “A Morgan Stanley index tracking emerging-market stocks is up 12% in dollar terms. By contrast, its index following stocks in developed markets outside the U.S. and Canada is down 9%.” Meanwhile, “The extra yield investors demand to own developing nation debt instead of U.S. Treasuries narrowed 10 basis points, or 0.1 percentage point, to 5.68 percentage points.
Emerging market currencies have also enjoyed a nice bounce, led by an across-the-board 7% gain in the Mexican Peso, Brazilian Real, and Russian Ruble over the last five weeks. Analysts at both Citigroup and Goldman Sachs are now encouraging clients to pile back into such currencies, evidently confident that the rally is sustainable: “Valuation has become very attractive in many cases, in particular in historically higher-yielding currencies.”
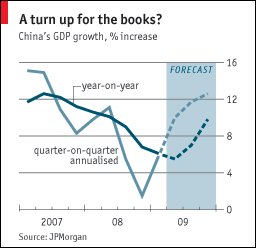
The concern, however, is that this rally is a product of financial and technical factors, and is not underlied by macroeconomic fundamentals. Exports and confidence have tumbled at a record pace, such that “J.P. Morgan forecasts at least 11 emerging economies — among them South Korea, Taiwan, Russia, Turkey, and Mexico — will shrink in 2009, with another 4 posting no growth.” Instead, investors are using low prices and a lull in bad news - rather than a change in economic tenor - as a basis for buying.
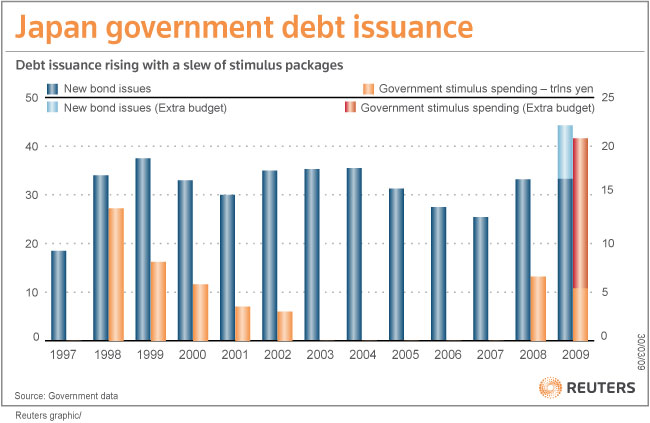
Of course, the bulls will selectively point to data which paint a different picture. “From monetary easing to joint fiscal policy to capital becoming less constrained at banks, the potential for a recovery in 2010 and 2011 seems more likely.” Some analysts have argued that they believe emerging markets have been, and will continued to be cushioned from the worst of the financial crisis due to their conservative financial sectors, but this argument strikes me as self-justification. Others point to the $500 Billion increase in capital that the IMF (via the G20) will potentially make available to developing countries. As I wrote in a recent post, however, much of the perceived increase is redundant and/or has not yet been guaranteed by rich countries.
Personally, I fall in the “cautiously pessimistic” camp, summarized as follows: “The economic picture is cloudy enough that a number of investors say it is worth adopting a more nimble approach in the short run.” In other words, a wait-and-see approach is probably more prudent than following the crowd, especially since it was the crowd that as originally responsible for the bubble.